TOO MUCH BLOOD?
Your body can sometimes make too many red blood cells, which causes your blood to thicken.
This condition is known as “polycythemia”
But what does this really mean, and why should you care?🤷🏽♂️
Check the thread
It happens when your bone marrow makes too many red blood cells.
The result? Blood that’s much thicker than it should be, making it difficult for your heart to pump efficiently.
✍🏽 Polycythemia Vera (PV) is the most common form of polycythemia.
PV It is a chronic blood cancer that causes your body to make too many red blood cells, often along with too many white blood cells and platelets.
The blood becomes too thick, leading to a higher risk of blood clots, strokes, and heart attacks.
If you have PV, you might experience:
– Constant headaches
– Feeling dizzy or light-headed
– High blood pressure
– A reddish tint to your skin, especially on your face
These signs shouldn’t be ignored, as they can lead to serious complications if left untreated
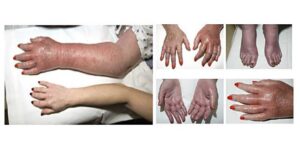
✍🏽 WHY IS PV DANGEROUS?
Because thick blood flows slowly, it can lead to blood clots that block blood flow.
This raises the risk of strokes, heart attacks, or even deep vein thrombosis (DVT), where clots form in the legs and travel to the lungs
Polycythemia can also have secondary causes
✍🏽 SECONDARY POLYCYTHEMIA
happens when your body needs more oxygen than usual.
Maybe you live at a high altitude, have lung problems, or suffer from sleep apnea.
In response, your body produces extra red blood cells to carry more oxygen, thickening your blood.
There is also:
✍🏽 RELATIVE POLYCYTHEMIA
This occurs when the liquid part of your blood (plasma) decreases, making it seem like there is too much blood.
This can happen if you’re dehydrated or losing fluid, making your blood thicker than normal
✍🏽 RISK FACTORS
– Polycythemia Vera is more common in people over 60
– Having relatives with polycythemia increases your risk.
– Smoking can lead to secondary polycythemia, as it lowers oxygen levels in your body.
– Lower oxygen levels can trigger more red blood cell production.
– Conditions that reduce oxygen in the body (COPD, sleep apnea, longterm carbon monoxide exposure) make it more likely to develop secondary polycythemia.
✍🏽 WHAT CAN BE DONE?
It requires medical attention, but treatments aim to reduce the number of red blood cells and thin the blood to lower the risk of clots. 🏥
– Phlebotomy to reduce blood thickness
– Medications can slow down the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Other medications can help thin the blood and lower the chance of blood clots forming.
✍🏽 HOW TO LOWER YOUR RISK
– Drinking plenty of water can help keep your blood at a normal consistency. 💧
– Avoid smoking as it can further thicken the blood and increase the risk of clots. 🚭
– If you have conditions like lung disease or sleep apnea, managing them can help reduce your risk of secondary polycythemia.
– Light physical activity can improve circulation and lower your risk of clot formation. 🏃♂️
It might sound surprising, but having too much blood can be just as dangerous as having too little. If you notice any signs of polycythemia or experience frequent symptoms like dizziness, headaches, or high blood pressure, it’s important to see your doctor for a blood test