Arthritis affects millions globally, bringing pain, stiffness, and swelling to the joints and impacting quality of life.
This is the most comprehensive thread on arthritis, from types and symptoms to causes, treatments, and prevention tips.
Scroll up to understand how to manage and even prevent this common condition.
A thread
🔑 WHAT IS ARTHRITIS?
Did you know that “Arthritis” is not one single disease? But a term for over many joint-related conditions causing pain and dysfunction.
It can strike at any age, though it is more common in adults over 60.
Some types progress slowly over years, while others appear quickly.
🔑 TYPES OF ARTHRITIS
-Osteoarthritis (OA)
Often called “wear-and-tear” arthritis, OA develops as joint cartilage wears down over time, leading to bones rubbing against each other. It mostly affects the knees, hips, and hands.
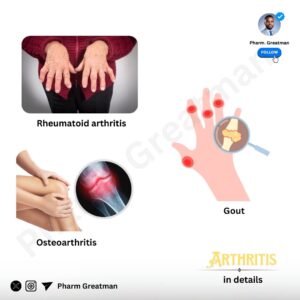
– Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
RA is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks joint linings, leading to pain, swelling, and eventual joint damage. Unlike OA, RA often affects both sides of the body (e.g., both wrists).
– Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Linked to the skin condition psoriasis, PsA causes joint pain and inflammation along with skin rashes. It often impacts fingers, toes, and spine and can vary in severity.
– Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, often caused by high-purine foods (like organ meat, sea foods..). Gout attacks are sudden, often affecting the big toe but can strike other joints.
– Ankylosing Spondylitis
A type of arthritis affecting the spine, it leads to pain and stiffness from the neck down to the lower back. Over time, vertebrae may fuse, resulting in a hunched posture.
🔑 COMMON SYMPTOMS
– Pain in and around joints, worsened with movement or activity.
– Swelling and stiffness, especially after rest.
– Reduced range of motion in the affected joints.
– Redness and warmth in inflammatory types like RA and gout.
– Joint deformity in severe or prolonged cases.
🔑 CAUSES OF ARTHRITIS
The different types of arthritis have different causes. Some are well understood, while others remain unclear as to their origin.
– Genetics
Family history can increase the risk, especially for RA and OA.
– Infections
Some bacterial or viral infections can trigger arthritis.
– Autoimmune response
In types like RA, the immune system mistakenly attacks joint tissues.
– Wear and tear
Aging, repetitive motion, or injury often leads to OA.
🔑 WHAT PUTS YOU AT RISK?
– Age
Older age increases the risk, especially for OA.
– Gender
Women are more likely to have RA, while men have a higher risk for gout.
– Weight
Extra weight puts more pressure on weight-bearing joints, like knees, and can worsen OA.
– Injury
Joint injuries from sports or accidents can increase the likelihood of arthritis later in life.
– Lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyles and diets high in red meat and sugary drinks can raise the risk for certain types like OA and gout.
🔑 ARTHRITIS IS NOT GUESSED, IT CAN BE DIAGNOSED
Every knee and joint pain may not be arthritis, get it examined, typically by:
– Your Medical History
A doctor will review symptoms, family history, and lifestyle.
– Your Physical Examination
Checking for swelling, warmth, and range of motion in joints.
– Imaging Tests
X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds can show cartilage damage, bone spurs, and joint alignment.
– Blood Tests
For RA or gout, blood tests can detect inflammation markers or elevated uric acid levels.
– Joint Fluid Analysis
A sample of joint fluid can help identify gout, infection, or specific forms of arthritis.
🔑 TREATMENT OPTIONS
– Medications
Pain relievers like NSAIDs can reduce pain and inflammation. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) used for RA to slow disease progression. For gout, medications control uric acid levels.
– Physical Therapy
Regular movement and exercise under a physical therapist’s guidance can strengthen muscles around the joints and improve flexibility.
– Exercise
Gentle, low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking reduce pain and keep joints flexible without overloading them.
– Diet and Nutrition
Anti-inflammatory diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3s can help control symptoms. Avoiding high-purine foods, like red meat and seafood, is essential for gout sufferers.
– Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on joints, especially in the knees and hips.
– Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat can relax muscles and relieve stiffness, while cold packs reduce swelling and numb sharp pain.
– Assistive Devices
Canes, braces, and ergonomic tools help take pressure off painful joints.
– Surgery
In severe cases, joint replacement (like knee or hip) or joint fusion may be options when other treatments are ineffective.
🔑 TOP TIPS, IF YOU ARE LIVING WITH ARTHRITIS
– Stay Active
Movement is essential, even if it’s gentle stretching. Long periods of inactivity can worsen stiffness.
– Sleep Well
A good night’s sleep supports recovery, and lack of sleep can intensify pain sensitivity.
– Avoid Smoking
Smoking worsens inflammation and is linked to higher RA risk.
– Practice Mindfulness
Relaxation techniques and stress management can ease the emotional toll of chronic pain.
🔑 IF YOU DON’T HAVE ARTHRITIS YET.. You can prevent it (mostly)
A sad reality is that some factors like age and genetics are not exactly preventable, however, these steps may lower your arthritis risk:
– Exercise Regularly
Stay active to keep joints flexible and muscles strong.
– Maintain a Healthy Weight
Reducing weight lowers stress on key joints, especially knees.
– Protect your Joints
Use proper techniques when lifting, and avoid repetitive stress on joints.
– Anti-inflammatory Diet
Eat a balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish. Some foods like processed foods can support joint inflammation
THERE ARE SOME APPROACHES FROM TRADITIONAL MEDICINES IN ARTHRITIS MANAGEMENT
– Tumeric
This yellow spice has a compound called curcumin that helps reduce swelling and pain. You can use it in cooking or take it as a supplement.
– Ginger
Often used in teas or cooking, ginger can help with inflammation and pain.
– Boswellia
Also known as frankincense, this herb is used in traditional medicine to lower swelling and improve joint movement.
– Willow Bark
Contains a natural chemical similar to aspirin, which can relieve pain. It can be taken as a tea or supplement.
OTHER APPROACHES INCLUDE
– DIET
Omega-3 Fatty Acids found in fish (like salmon) and flaxseeds, these healthy fats can help reduce inflammation in the body
Eating a variety of colorful fruits and veggies can provide antioxidants that may help reduce swelling.
A Mediterranean Diet, which is an eating pattern includes healthy fats (like olive oil), whole grains, fish, and lots of plant foods, which may lower inflammation.
– ACUPUNCTURE
A practice from Chinese medicine where thin needles are placed in specific points on the body to relieve pain.
– MASSAGE THERAPY
GENTLE massage can help relax muscles around joints and improve blood flow, which may ease pain.
– YOGA AND TAI CHI
These gentle exercises involve slow movements and stretching, which can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in joints.