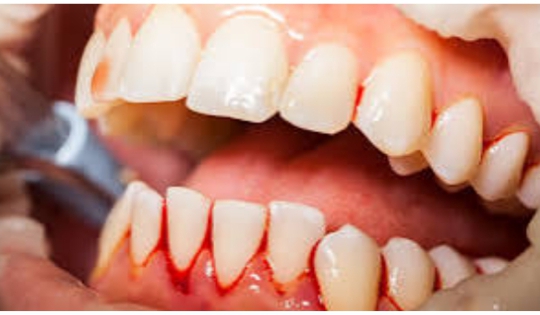
Dental Bleeding: Why Your Gums Might Be Bleeding and What to Do About It🦷🩸
Have you noticed blood on your toothbrush or while flossing?
It might seem minor, but bleeding gums could be trying to tell you something about your oral health!
A thread 👇
What Causes Dental Bleeding? 🤔
1. Gingivitis (Early Gum Disease)🦠
▫️What it is: Inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup along the gumline.
▫️Why it matters: Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that irritates the gums, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding,
especially during brushing or flossing. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more serious gum disease (periodontitis).
2. Aggressive Brushing or Flossing🪥
▫️What it is: Overzealous brushing or flossing can damage the delicate tissues of your gums.
▫️Why it matters: While brushing and flossing are essential for good dental health, doing so too harshly can cause microtears in your gums, leading to bleeding.
3. Periodontitis (Advanced Gum Disease) 🚨
▫️What it is: A more severe form of gum disease where the inflammation
spreads deeper into the gums and bone, leading to gum recession, loose teeth and tooth loss.
▫️Why it matters: Without treatment, periodontitis can cause irreversible damage to the gums and bones that support your teeth. Frequent gum bleeding is a red flag for this condition.
4. Vitamin Deficiencies 🥦
▫️What it is: Lack of certain vitamins, particularly vitamin C & vitamin K, can lead to weakened gums & increased bleeding.
▫️Why it matters: Vitamin C is crucial for maintaining healthy gums and blood vessels, while vitamin K helps in blood clotting.
5. Hormonal Changes 🔄
▫️What it is: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make your gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding
▫️Why it matters: During pregnancy, some women develop “pregnancy gingivitis” due to increased blood flow to the gums,
making them more susceptible to irritation and bleeding.
6. Medications 💊
▫️What it is: Certain medications, such as blood thinners (e.g., aspirin, warfarin), can affect your blood’s ability to clot and cause your gums to bleed more easily.
▫️Why it matters: If you’re on any medication that affects blood clotting, it’s important to inform your dentist, as this could increase your risk of bleeding during dental procedures
7. Poor Oral Hygiene🧼
▫️What it is: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar, increasing your risk of gum inflammation and bleeding.
▫️Why it matters: Good oral hygiene is key to preventing gum problems. Failing to brush or floss regularly allows bacteria to accumulate, leading to gingivitis and gum disease.
How to Stop Gum Bleeding 🛑
1. Improve Your Oral Hygiene Routine 🪥
▫️Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
▫️Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque between teeth.
▫️Use an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
2. Use a Soft Toothbrush 🧼
▫️Switch to a soft-bristled toothbrush to reduce trauma to your gums. Be gentle while brushing, using circular motions rather than aggressive back-and-forth strokes.
3. Visit Your Dentist Regularly 🦷
▫️Get a professional cleaning at least twice a year to remove plaque and tartar that can’t be cleaned at home.
▫️If you notice persistent bleeding, schedule an appointment with your dentist or dental hygienist for an evaluation.
Early detection is key to preventing more serious gum issues.
4. Boost Your Vitamin Intake 🥕
▫️Incorporate foods rich in vitamin C (citrus fruits, berries, spinach) and vitamin K (leafy greens, broccoli) into your diet to strengthen your gums and promote healing
5. Avoid Smoking 🚬
▫️Smoking weakens your immune system and reduces blood flow to the gums, making them more prone to infections and bleeding. Quitting smoking can significantly improve your gum health.
6. Consider Changing Medications (If Needed) 💊
▫️If your gums are bleeding due to medications like blood thinners, consult your doctor or dentist.