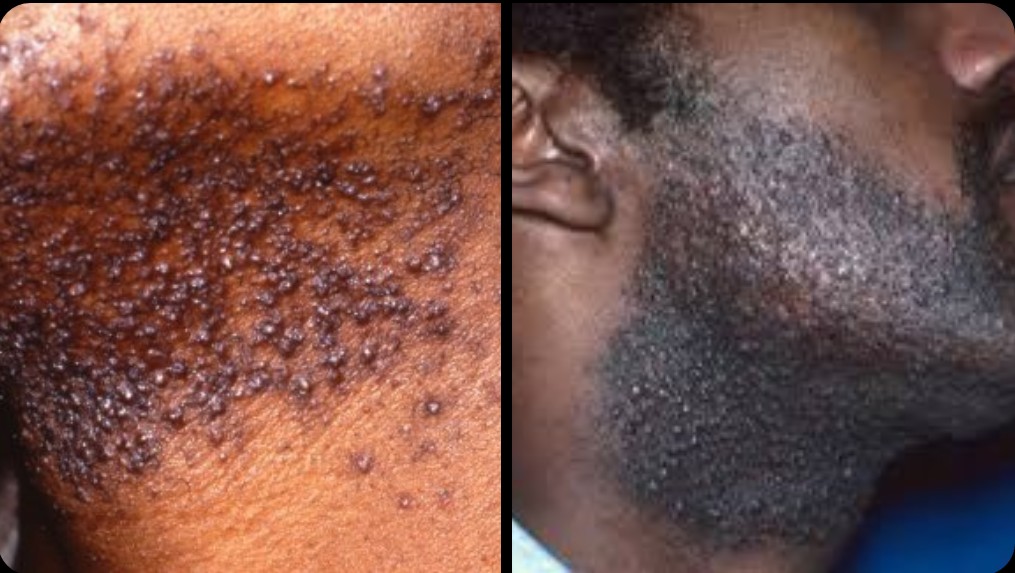
Razor bumps could either be a mere skin irritation or an infection of the skin.
Due to poor diagnosis, it is often undertreated or treated wrongly.
When it happens due to a skin infection, it is called FOLLICULUTIS
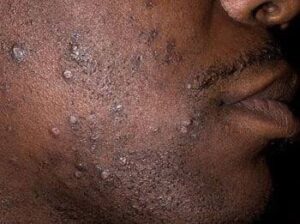
When it is merely due to irritation from shaving, it is called PSEUDOFOLLICULITIS BARBAE (PFB)
Our interest today is Pseudofolliculitis barbea, also known as razor bumps.
🍭What is Pseudofolliculitis Barbae?
It is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that results from shaving
The most commonly affected shaving practice is the shaving of beards
However, it can also affect other places like; the armpit, groin, and legs when shaved frequently.
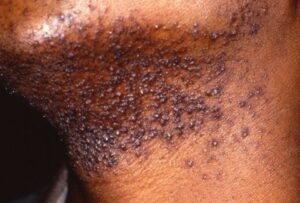
🍭WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF PFB?
•Itching and stinging few days after shaving
•Inflamed skin bumps known as erythematous papules
•Bumps may be seen on the neck, cheeks and chin
•Pain while shaving
•Pus-filled lesions may occur if infection sets in
•Darkening of affected area
•Raised scars that may appear thick ( hypertrophic scarring)
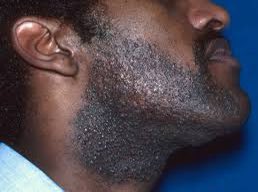
🍭WHAT ARE THE CAUSES?
PFB develops after shaving or hair removal by other methods
It occurs when freshly shaved hair decides to evade the natural pattern of regrowth
Now, instead of growing out of the hair follicle, they curl on themselves, move away from the follicles and penetrate the skin.
This abnormal pattern is called Extrafollicular penetration
In some cases, the hairs do not grow out through the skin
They rather decide to grow downwards into the dermis
This style of growth is called Transfollicular penetration.
Regardless of which abnormal pattern the hair chooses to grow, both processes lead to an inflammatory reaction.
This reaction brings out the visible skin lesions as seen in the beard area of many men.
🍭WHO IS AT RISK?
PFB is most common in people with naturally coarse hair or people with tightly coiled hair.
The reason is because this kind of hair can easily twist back into the skin
This is why it’s common among Africans
People who shave regularly are also at risk
People with a family history of PFB are also at more risk.
🍭PFB can lead to some health complications like;
•Secondary bacterial infection
•Skin colour change that may become a cosmetic concern
•Hypertrophic scarring
🍭HOW IS IT PFB DIAGNOSED?
It is usually detected by physical examination
Sometimes a Doctor may use a dermatoscope to properly view ingrown hair under the skin surface
When an infected is present, a swab will be taken from the pus-filled bumps and tested
HOW IS PFB TREATED?
The treatment of PFB is easy, but not many people are comfortable with the approach.
Hence, they try different methods that often yield little or no effect.
Let’s see some approaches 👇
🍭When done consistently, these methods can improve PFB;
•Make hair soft with warm water before shaving
•Wash beards clean first before shaving
•Use wet shaving method; may be expensive but, better for sensitive skin prone to PFB
•Wet beards with shave cream or gel and shave
•One of the recommendations for high-risk people is to avoid regular shaving to allow the hair to grow out
•Allowing for about 3-4weeks before shaving the affected area is advised
But in a situation where this is not feasible, other methods include ;
👇
•Using clippers to trim hair without making direct skin contact
•Grooming technique; maintaining hair length of about 0.5cm
•Shaving in the direction of hair growth
•Avoiding pulling or stretching the skin when shaving
•Depending on the severity and extent of lesions, your doctor may recommend topical steroids and antibiotic creams to apply on the affected area.
•In mild cases, topical retinoids and benzyl peroxide creams may also used
•Skin Peels containing glycolic and salicylic acids may be used to prevent ingrown hairs
•Laser hair removal therapy is one of the most effective method and your doctor would decide which one is safe for your hair type